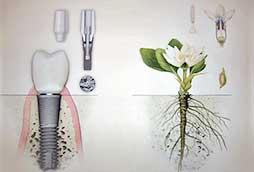
 The word implant originates from the Latin name "plantum" and means a graft that is placed in the jawbones and becomes part of it, without any problems and for a long time replaces the lost teeth and becomes a new support for artificial crowns, bridges and other types of dentures.
The word implant originates from the Latin name "plantum" and means a graft that is placed in the jawbones and becomes part of it, without any problems and for a long time replaces the lost teeth and becomes a new support for artificial crowns, bridges and other types of dentures.
Regardless of the cause of tooth or teeth loss (due to chronic or acute inflammation, trauma, periodontal disease), you have the choice of restoring normal food chewing, good aesthetics and proper phonetics through fixed bridges over your natural teeth or removable dentures, notably by placing a dental implant.
Due to the great successes and small complications, implant placement is gaining popularity worldwide. These successes are the result of continuous research and practices in the methods of their placement.
Stable mechanical connection between implant and bone (osteointegration) depends on:
1. The condition of the bone;
2. Implant design and parameters: (macroscopic design of the implant body);
3. Treatment of the implant surface: (Microscopic design of the implant body);
4. Precise and reliable surgical technique.
With the development of science and technology, dental implantology undergoes a very rapid development, consistent with osteointegration. Various implantation systems are available, varying in shape and design, and other parameters.
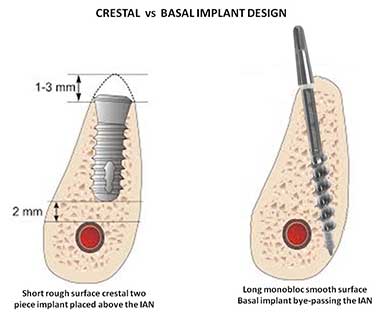

Implant classification:
 1. According to the form (root, screw);
1. According to the form (root, screw);
2. According to the material (titanium, bioceramic);
3. According to the surface (smooth polished, rough retentive);
4. According to time of implantation (early-imediate, late);
5. According to the method of implantation (single-stage-closed, two-stage-open);
6. According to the position in the bone (spongy, bicortical).
In practice, the most widely used species to be implanted is the screw-type intraosal titanium implant. It is lightweight, biocompatible, highly resistant to fracture and resistant to corrosion.
Implantation methods:
One-stage closed implantation (Immediate loading implantation):
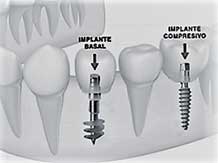 An innovative method using one-piece implants (the implant and superstructure are monolithic).
An innovative method using one-piece implants (the implant and superstructure are monolithic).
The implant is placed (anchored) directly into a compact bone (hard bone), in the alveolar, immediately after removal of the tooth.
Without waiting for a period of osteointegration, the implant can be immediately loaded with bridge structures (early loading).
Two-stage open implantation - (Conventional implantation):
A classical universal method is the two-stage late-load implantation where, after the implant is placed into the spongy bone, a period of 3-5 months (a required osteointegration period) is required, so the implant can be adequately loaded with a crown or bridge construction.
Successful implantation depends on:
1. Patient's side (type, volume and location of the implant placed in the bone, accompanying diseases, harmful habits and hygiene);
2. Implantologist and clinic (theoretical and practical skills, manual skills, protocol and implantation, and strict observance of septic and antiseptic principles);
3. Implants and implantation system (made of medical titanium of world-famous brand, possessing all international quality certificates).
Complications of implantation are:
1. An infection obtained around the surface of the implants (periimplantitis) that causes them to be rejected. This condition has a higher incidence in conventional dental implants.
2. Swelling, bleeding, numbness are rare complications and depend on the general condition of the patient as well as on the local oral condition, the implant sites and to a large extent on the experience of the implantologist and the type of surgical technique and methods used in implantation.